Setting out technical division of responsibilities
Technical demarcation sets out the technical division of responsibilities between the commissioning party and the contractor. It makes it clear exactly what the two contracting parties have to do. This is important in the case of semi-public and private charging infrastructure, because with these types of infrastructure, contractors make use of the commissioning party’s grid connections, electrical installations and buildings and land.
Charging infrastructure is largely made up of five components. This demarcation lets you know who is responsible for which component:
- The recharging station/column to which electric vehicle (EV) drivers connect their charging cable to start charging.
- The cabling from the recharging station to the existing electricity grid or an existing electrical installation.
- A grid connection.
- A lockable cabinet. The power cable to the recharging stations runs into this cabinet, and equipment, safety devices and switches are also installed here for control, monitoring, power distribution and the subsidiary distribution of power to the recharging stations/columns.
- Layout of the car park.
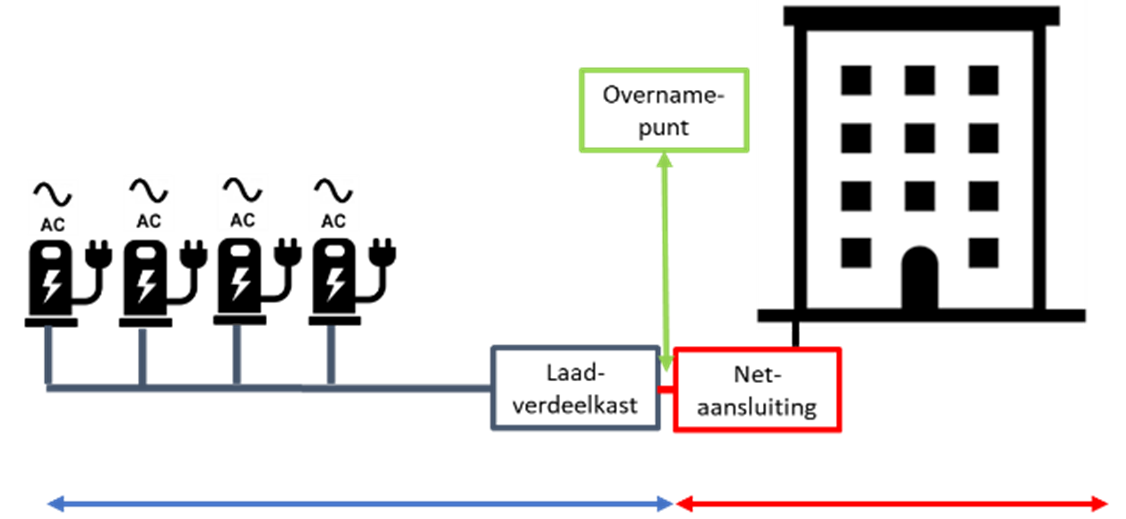
The figure below gives a schematic representation of the demarcation for semi-public charging infrastructure. The charging infrastructure is connected to a building’s existing electrical installation. A ‘takeover point’ has been added here. This marks the separation of responsibilities:
- the contractor installs the charging stations and cabling;
- the contractor installs the power distribution box;
- the commissioning party manages (or arranges the management of) the existing electrical installation and supplies power to the charging stations via a connection to the distribution box.
Things to consider
The division of responsibility for the five components mentioned above should be laid down. In other words: where is the takeover point? Determining the takeover point is particularly important in the case of semi-public and private charging infrastructure. When determining the takeover point, the following points should be considered:
- To what extent does the commissioning authority intend to carry out modifications to the electrical installation of the existing building or land?
- Who is responsible for the existing electrical installation and who is responsible for the charging infrastructure?
- Investment can vary considerably, especially in the semi-public sphere. The distance between the charging points and the electrical installation is very important in this respect.
Example guidelines and reference projects
